Lysosomal storage diseases (LSDs) are a group of more than 70 rare inherited metabolic disorders caused by the malfunction of lysosomal enzymes. These enzymes are responsible for breaking down various substances in cells. When they fail, harmful materials accumulate in lysosomes, leading to cellular dysfunction, progressive organ damage, and, in many cases, life-threatening complications.
Request a sample copy of this report at: https://www.datamintelligence.com/download-sample/liposomal-supplements-market
A Complex and Underdiagnosed Category of Rare Genetic Disorders
LSDs affect approximately 1 in 5,000 to 1 in 10,000 live births worldwide. Despite being individually rare, their collective impact is significant. Common forms include:
• Gaucher disease
• Fabry disease
• Pompe disease
• Tay-Sachs disease
• Niemann-Pick disease
• Mucopolysaccharidoses (MPS)
Diagnosis is often delayed due to non-specific symptoms and limited awareness among clinicians, especially in regions with fewer resources. Genetic screening, enzyme assays, and advanced imaging are now helping shorten diagnostic timelines.
Long-Term Disease Management: Challenges and Evolving Strategies
Treatment for lysosomal storage disorders varies depending on the specific disease and symptom severity. Historically, supportive care was the only option. However, three major therapeutic strategies have emerged:
1. Enzyme Replacement Therapy (ERT): Synthetic enzymes are administered intravenously to compensate for the missing or malfunctioning enzyme.
2. Substrate Reduction Therapy (SRT): These oral drugs aim to reduce the production of toxic substrates that build up due to enzyme deficiency.
3. Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (HSCT): In some diseases, this approach can help restore enzyme activity.
While ERT has revolutionized LSD treatment, it comes with challenges: high costs, immune reactions, limited blood-brain barrier penetration, and the need for lifelong infusions.
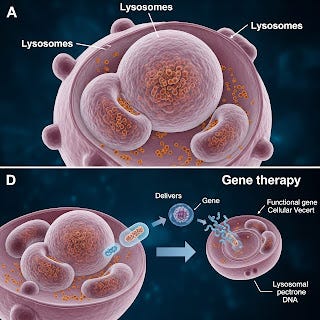
Breakthroughs in Gene Therapy for Lysosomal Storage Disorders
The future of LSD treatment lies in gene therapy for rare inherited lysosomal disorders. AAV and lentiviral vector platforms are showing promising results in preclinical and early-stage human trials. Gene therapies aim to provide a one-time curative option by correcting the underlying genetic defect. For example:
• Avrobio and Passage Bio are advancing trials for Fabry and GM1 gangliosidosis, respectively.
• CNS-targeted delivery systems are being developed for neuronopathic forms of LSDs.
• This marks a critical step toward durable solutions, particularly for neurologically progressive forms previously considered untreatable.
Read the full CI Insights report: https://www.datamintelligence.com/research-report/liposomal-doxorubicin-market
Global Access, Equity, and Health Policy Considerations
Access to LSD therapies remains uneven, especially in low- and middle-income countries. The high cost of treatments like ERT (often exceeding $200,000/year per patient) limits their global reach. Governments and health systems are now exploring pricing negotiations, orphan drug designations, and rare disease policy frameworks to expand treatment access.
Global organizations are also pushing for expanded newborn screening for lysosomal storage diseases, which is crucial for early diagnosis and intervention.
About DataM Intelligence
DataM Intelligence 4Market Research LLP is a trusted provider of healthcare competitive intelligence (CI), specializing in tracking CGT innovations, clinical trials, regulatory shifts, and commercial strategies. Our custom research services cover:
• Cell and gene therapy market forecasting
• Competitive pipeline tracking
• Regulatory intelligence (FDA, EMA, PMDA)
• Opportunity analysis and pricing strategies
• Clinical and commercial due diligence
???? Visit: www.datamintelligence.com
Comments on “Precision in Rare Disease: Competitive Insights into the Future of Lysosomal Storage Disorders”